Electric motor efficiency has a significant impact on the industrial, consumer, and automotive sectors. Increased efficiency leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions through a reduction in power consumption and increased range between charges - for everything from EV’s to your power tools. With electrification continuing to accelerate across our day-to-day living, many wonder what type of motor is best suited to meet these modern day demands.
Historically, the induction motor was the go-to motor design because it was readily available and is a longstanding, proven technology. However, the intrinsic design of the induction motor requiring a slip between rotor and stator will always limit efficiency. With recent advances in permanent magnet materials (energy density), and manufacturing, today’s permanent magnet motor designs take performance and energy efficiency usage to new levels not possible with the induction design.
Let’s take a deeper dive into both motor designs which then supports the choice of a permanent magnet design over that of the induction motor design. Equally important, understanding how Soft Magnetic Composites (SMC) can transform not only the traditional radial flux design, but new topologies that are driving tomorrows designs and performance levels with reduced heat generation and a more efficient use of copper and magnet material.
Here are a few things to consider when exploring induction vs. permanent magnet motors:
- Cost
- Efficiency -- torque, core losses, frequency & motor speed control
- Material opportunities
- Application
Permanent Magnet Motor vs. Induction Motor Efficiency
The figure below shows the general layout of both the Permanent Magnet motor (on the left) and the induction motor (on the right). In the permanent magnet design, the rotor contains a series of magnets either internal or external to the OD of the rotor. The stator is wound with copper wire creating a magnetic field that interacts with the rotors permanent magnets resulting in rotation and torque. Compare this to the induction motor where rotor and stator are traditionally stamped lamination steel with the motor windings only on the stator which induces an opposing magnetic field in the rotor. This interaction results in rotational torque.
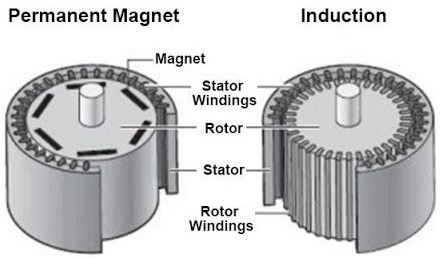
(Comparison of AC induction motor design vs. permanent magnet motor)
Modern high torque motors whether permanent magnet or induction design use three-phase applied current. The three-phase design offers inherently better efficiency and is also self-starting. If the motor is designed to operate at a fixed rotational speed, then the number of stator poles can be adjusted to give the desired speed at the typical fixed frequency of 50 or 60 Hz. For these types of applications, the laminated induction motor is probably the most frequently chosen alternative. However, what if you want to have a variable speed motor? In this configuration, you would need to incorporate a variable frequency power supply to facilitate the variable speed. Although an induction motor would work, in this design, the permanent magnet design offers enhanced performance with greater flexibility.
The fine details of electric motor design are more complex than described below, but this is a great head start for those weighing their options between an induction and permanent magnet motor design.
Permanent Magnet Motor Efficiency
The inherent efficiency of a permanent magnet motor is higher than an induction motor – eliminating the intrinsic lag of the applied and induced field. Permanent magnet motor run synchronously with the applied frequency - allowing the motor to operate at a speed set by the frequency drive. As you increase the frequency, total losses in induction motors will be far greater than in permanent magnet motors – having efficiencies up to 97.5%.
A 50 kW (about 70 HP) permanent motor typically weighs less than 30 lbs. At any given frequency, the rotational speed of the permanent magnet motor is always greater than that of its induction counterpart due to the inherent slippage necessary in the induction design. The synchronous speed can be represented by the following equation:
Ns = 120 * frequency / pole count
(Ns is synchronous speed. Pole count is the total pole count per phase, including both the north and south poles)
Today, permanent magnet motors are used in applications and platforms such as - the Ford Mustang Mach-E, BMW, Ultium Platforms, Tesla, high efficiency variable frequency HVAC motors, battery powered hand tools and drones...Did you spot the trend here – everything that is battery powered or dependent upon high efficiency, is a 3 phase permanent magnet motor.
Induction Motors:
As noted earlier, an induction motor operates by the stator winding inducing an opposing current in the rotor (thus creating a magnetic field). That opposing field results in rotor rotation. The lag between the applied stator current and resultant rotor opposing field results in slippage between the applied field and rotation. The maximum speed of an induction motor is represented by the same equation as for the permanent magnet motor. However, inherent with induction is the requirement for slippage (asynchronous operation). As shown in the figure below, when the amount of slip in an induction motor approaches zero, the torque generated also goes to zero. Thus, it is impossible to operate an induction motor synchronously. For example, a two pole AC induction motor operating at 60 Hz will have a synchronous speed of 3600 RPM but there is typically a 5% loss in speed due to the slippage; thus, the maximum motor speed will be about 3400 / 3500 RPM. This intrinsic design characteristic limits the maximum efficiency of the induction motor to about 90- 93%. 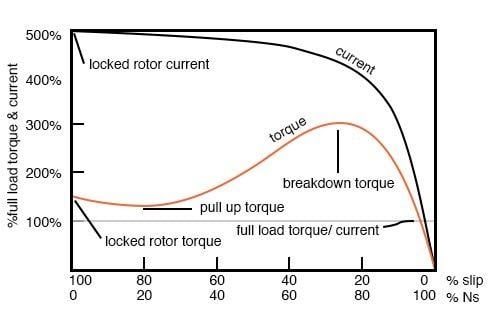
The maximum efficiency of an induction motor is 90 / 93% whereas that of a permanent magnet motor is at 97% plus. Although a 4 to 7% improvement doesn’t seem like a lot - imagine the cost of operation over a 10 year or more life span and that relatively small improvement in efficiency results in a considerable energy savings with reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Remember when we mentioned a 50 kW (about 70 HP) permanent motor typically weighs less than 30 lbs? Well, the weight of a typical 75 horsepower induction motor can exceed 500 pounds! Think of the implications this has for an automobile – the weight reduction is significant and has a multiplying effect on the total weight of the vehicle.
Cost Vs. Performance
One major consideration in permanent magnet motors is the cost of the magnets. If you’ve used high-energy magnets (such as iron neodymium boron), you’ve felt the pain in your budget (or your boss has). The potential waste of stamping the lamination material only compounds the problem.
Opportunities for powder metallurgy are abundant in these types of motors. The rotors of a permanent magnet motor can be made via sintered powder metal, regardless of whether you’re taking the internal or external design route. The stator can also be produced via soft magnetic composites. At the high switching frequencies expected, the losses in SMCs are lower than that of laminated 3% silicon iron, further improving the efficiency of this design. Simply put, soft magnetic composites are custom-built for high frequencies.
There’s an opportunity for powdered metal to provide additional efficiency to a permanent magnet motor vs. an induction motor. The 3D shape-making capabilities of powder metallurgy allow you to form the stator to totally encase all the wire in soft magnetic composite to eliminate end turn losses.
These are some of the many advantages that powder metal -- both sintered soft magnetic materials and SMCs -- offers.
Induction Vs. Permanent Magnet Motor Efficiency: The Winner Is...
The clear winner here is the permanent magnet motor. Now, couple the permanent magnet motor, with a unique topology enabled by Soft Magnetic Composite (SMC) technology and your motor will be lighter and more efficient, with a higher torque density and lower bill of material cost – all while reducing supply chain complications and using a sustainable manufacturing process.
If you need help designing the components to fully leverage the full potential of powder metallurgy for an AC or DC magnetic applications, contact us and check out our resource hub:
(Editor's note: This article was originally published in April 2020 and was updated on November 29, 2022 and July 27, 2023)



